Ethernet Splitter vs Switch: Which One Do You Really Need?
Ethernet splitter and Ethernet switches were created to fulfill the essential function of providing additional network port connections. However, as technology has advanced, the differences between these devices have become more pronounced, leading to varying market shares. For those unfamiliar with these technologies, distinguishing between them can be challenging, making it difficult to select the right product to meet specific needs. In this article, we will delve into the working principles of Ethernet splitters and switches, highlight their differences, and offer guidance on how to choose the right device to meet your requirements.
The Fundamental Differences Between the Switch and Ethernet Splitter
Working principles
An Ethernet splitter connects to network cables and initially supported only 100 Mbps speeds. However, advancements have allowed newer versions to support up to 1 Gbps. A standard Cat5e cable consists of 8 copper wires. When transmitting at a speed of 100 Mbps, only 4 of these wires are used: the orange-white/orange pair is used for sending data, while the green-white/green pair is used for receiving data. When operating at Gigabit speeds, all 8 wires are utilized. An Ethernet splitter divides the 8 copper wires into two separate Ethernet links. Each of these links operates independently, so the available bandwidth is shared equally. For instance, if a 100 Mbps Ethernet link is split using a splitter, it will result in two links, each with a bandwidth of 50 Mbps. Importantly, the Ethernet splitter does not process network traffic; it merely functions at the physical layer of the network.
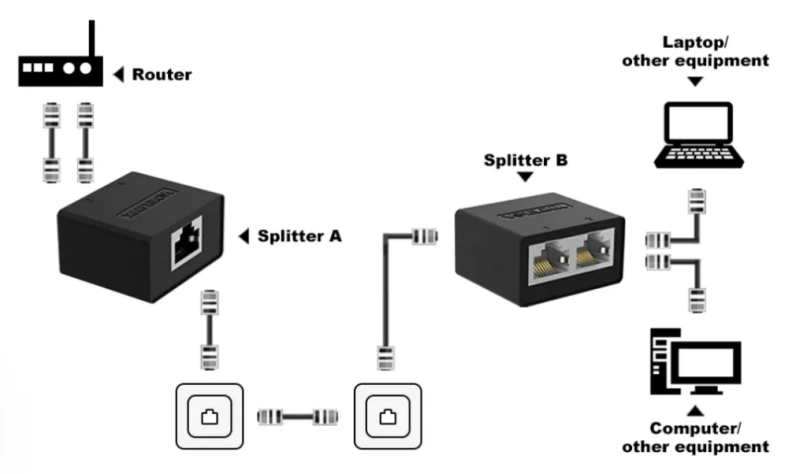
An Ethernet switch forwards data using a MAC address table. Each device is assigned a unique MAC address when it leaves the factory. The switch automatically records the MAC address of each device connected to its ports, creating a MAC address table. When Device A sends data to Device B, the switch reads the target MAC address in the data frame. It then queries its MAC address table, identifies the corresponding port, and forwards the data exclusively to that target port (other ports do not receive the data). If the switch encounters a MAC address that it doesn’t recognize, it broadcasts the received data frame to all ports except the one from which it was received. The Ethernet switch operates at the data link layer, handling traffic as it expands network ports. There are also Layer 3 switches that function at the network layer.

Comparison of performance and advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the Ethernet splitter
- Low Cost: You can purchase a reliable Ethernet splitter for just $4 to $5.
- Easy Installation: Ethernet splitters are plug-and-play devices, meaning they require no configuration or complex setup.
- Low Transmission Latency: Since the Ethernet splitter only broadcasts traffic and does not manipulate it, the transmission latency is very low. This latency is primarily influenced by the quality of the network cable used.
Disadvantages of the Ethernet splitter
- Need for Pairing: Ethernet splitters must be used in pairs. Their working principle is akin to a “split line that does not split the flow.” This means that when lines are split, they must be paired to maintain normal communication.
- Limited Device Support: An Ethernet splitter supports a maximum of two connected devices. This limitation is due to the physical structure of the network cable, which consists of only eight copper wires. The Ethernet splitter can only divide two network ports and cannot be expanded for additional devices.
- Reduced Bandwidth and Transmission Distance: The bandwidth and transmission distance are effectively halved when using an Ethernet splitter. For example, a standard connection of 100 Mbps would be divided into two connections of 50 Mbps each. Similarly, for a Gigabit connection of 1000 Mbps, the bandwidth would reduce to 500 Mbps for each device. Additionally, the effective transmission distance is reduced, as electromagnetic interference can impact signal quality when the bandwidth is split.
- Lack of Communication Between Ports: Ethernet splitters do not support traffic forwarding, meaning the ports are physically isolated from one another and cannot communicate with each other.

Advantages of Ethernet switches
- Independent Bandwidth for Each Port: Each port operates with its own bandwidth, allowing all ports to function at their full nominal rate. This setup can prevent network congestion.
- Strong Scalability: Ethernet switches can connect dozens of devices, and even hundreds of devices can be connected through stacking, Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation (MLAG), and other technologies.
- Improved Signal Quality: Traffic is retimed and shaped during transmission, which enhances signal quality.
- Reduced Transmission Delay: Each port can communicate with others, minimizing transmission delays.
- Versatile Configurations: Various configurations enable the implementation of complex functions, allowing the switch to meet different business needs effectively (especially in managed switches).
Disadvantages of Ethernet switches
- High Costs: even the most affordable managed switches typically start in the tens of dollars range.
- High Threshold for Use: Various functions of the switch need to be configured separately, requiring users to have high technical capabilities to configure them.
- Delay: The delay is higher than that of Ethernet distributors. The switch needs to operate the traffic, and there will inevitably be a delay. After the development of technology, this delay is currently in the microsecond level, which is completely imperceptible during use.

Applicable people
An Ethernet splitter is designed for connecting only two devices, making it suitable for short distances and low network speed requirements. It provides more network ports at a very low cost. Ethernet switches, on the other hand, come in various types that cater to all usage scenarios, including home networks, enterprise office networks, industrial production networks, and data center networks. You can find switches in all of these environments. In today’s network landscape, switches have become an essential cornerstone of networking.
Scenario-based Choice: Ethernet Splitter vs. Ethernet Switch, Which is More Suitable for Your Needs?
Home and small office
If you choose an Ethernet splitter, you will benefit from a low-cost network solution with a plug-and-play setup, along with simple network wiring and installation. On the other hand, if you opt for an Ethernet switch, you can connect multiple devices, enjoy 4K streaming without lag, and take advantage of various features for a superior network surfing experience.
Enterprises and data centers
In the context of enterprises and data centers, Ethernet splitters are no longer sufficient to meet network requirements. This is where Ethernet switches come into play. These switches support features such as VLAN isolation, MSTP, OSPF, and VxLAN, which are essential for fulfilling the basic needs of a modern network. They accommodate a variety of network topologies, enabling enterprises and data centers to configure their networks according to specific requirements. Additionally, Ethernet switches offer robust traffic forwarding performance, which can eliminate the risk of network congestion. Their strong scalability allows for network upgrades at any time without concerns about interruptions. These benefits have made the switch undeniable.
Market Trend: Technical Development Direction of Ethernet Splitter and Ethernet Switches
Technical development direction
The technical development of Ethernet splitters has stagnated since the introduction of switches. Due to inherent limitations in their working principle, Ethernet splitters cannot support an expansion of additional network ports, nor can they improve data rates. As a result, they are only applicable in low-speed usage scenarios. In contrast, Ethernet switches have seen significant advancements, especially with the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI). The latest generation of NPO switches has now entered the commercial stage, with single-port rates reaching terabits per second (Tbps). As technology progresses, we can expect switches with higher speeds, greater density, lower power consumption, and reduced costs. I believe that these advancements are not too far off.
Market selection
The Ethernet splitter is becoming increasingly rare in the market, with its presence mostly confined to ultra-low-price segments. In low-rate scenarios where fewer devices are used, Ethernet splitters still have limited application. However, even in these cases, small unmanaged switches are beginning to capture more of the market share previously held by Ethernet splitters. It is likely that in the future, Ethernet splitters may not even be mentioned in discussions about networking equipment. On the other hand, Ethernet switches are thriving in both consumer and enterprise markets. They are an indispensable part of network infrastructure; wherever there is a network, you are bound to encounter a switch. The evolution of the network is closely tied to the development of switches, which continue to advance in capability and functionality.

Purchase Decision Guide
Define your needs
When selecting a product, the first step is to determine the number of network devices you have.
- If you have fewer than two devices, a tight budget and don’t require high-speed connectivity, an Ethernet splitter is the more suitable option.
- If you have more than three devices and need greater transmission bandwidth, a switch would be more appropriate.
Determine the core parameters
After clarifying our needs, we can choose to buy either an Ethernet splitter or an Ethernet switch. If we decide to purchase an Ethernet splitter, we need to consider the material of the cable and the type of interface. A minimum of Cat5e cable should be used to ensure adequate transmission. Additionally, the interface of the Ethernet splitter should be gold-plated and resistant to oxidation to minimize maintenance in the future.
If we opt for an Ethernet switch, we must evaluate several aspects, including the number of ports required, whether a managed switch is necessary, if the switch supports Power over Ethernet (PoE), and if we prefer a fanless, silent option. By considering all these parameters, we can select the most suitable switch for our needs and enjoy an optimal Internet experience.
Brand and after-sales service
There are many brands selling switches on the market, and the quality of these switches can vary significantly. Choosing a reputable brand can help reduce the likelihood of after-sales issues and enhance the overall customer experience. In the high-end market, Huawei and Cisco are leaders, while in the lower-end consumer segment, TP-Link and LSOLINK are preferred choices for cost-effective solutions. LSOLINK offers a wide range of professional switch products to meet various network application needs. We have a dedicated technical support team available 24/7 to provide technical assistance and lifelong after-sales support. Our commitment to creating high-quality products and establishing a strong brand is unwavering.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can a switch completely replace an Ethernet splitter?
A: Yes, a switch can fully replace an Ethernet splitter, offering more ports and additional features.
Q: What should I be aware of when using an Ethernet splitter?
A: Keep in mind that Ethernet splitters must be used in pairs. They will halve the transmission bandwidth and distance, which can lead to network congestion if the traffic is heavy.
Q: Can switches be connected to Ethernet splitters?
A: Yes, switches can be connected to Ethernet splitters and will function properly since both are standard Ethernet devices.
Q: Can I use an Ethernet splitter to expand my network?
A: Yes, if you have fewer than two devices. However, if you have more than two devices, it is recommended to use a switch, as it is better suited for network expansion.
Q: What advantages do Ethernet switches have over Ethernet splitters?
A: For professionals, switches allow for more direct network management. For non-professionals, switches offer more network ports, faster speeds, and greater coverage without reducing network speed.
In This Article
- 1 The Fundamental Differences Between the Switch and Ethernet Splitter
- 2 Scenario-based Choice: Ethernet Splitter vs. Ethernet Switch, Which is More Suitable for Your Needs?
- 3 Market Trend: Technical Development Direction of Ethernet Splitter and Ethernet Switches
- 4 Purchase Decision Guide
- 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Show All
Collapse








