How to Select the Best 50ft Ethernet Cable for Your Needs?
The Basics of 50ft Ethernet Cable
Characteristics of 50ft Ethernet Cable
Choosing the right Ethernet cable is crucial when establishing a stable network connection. 50ft (approximately 15.24m) Ethernet cables offer a perfect compromise, balancing reach and flexibility. They’ve become a popular choice for homes, offices, and even small and medium-sized projects. This length avoids the hassle of frequent cable runs over short distances while also avoiding the signal attenuation and cost associated with longer cables.
The core advantage of 50ft Ethernet cables lies in the performance balance they offer at this “golden distance.” Physically, this length allows them to span multiple rooms or cubicles without the risk of structural damage from excessive bending or stretching. From a signal transmission perspective, 50ft is far shorter than the 100m maximum transmission distance specified by the Ethernet standard, eliminating the need for additional signal amplification equipment to maintain a stable connection. However, it’s important to note that the cable’s material and construction directly impact actual performance, as discussed in detail later.
The Difference Between Cables and Wires
When shopping, you may find some called “Ethernet cords” and others called “Ethernet cables.” Technically, there’s no strict distinction between the two; subtle differences exist in practical scenarios.
Ethernet cords: These are more targeted at structured cabling scenarios, emphasizing professional-grade transmission media that adhere to industry standards. These products are often clearly labeled with the cable category, such as Cat5e or Cat6, emphasizing professionalism.
Ethernet cables: This term is more consumer-oriented, often referring to plug-and-play, off-the-shelf cables. It emphasizes flexibility and convenience, and is more aligned with consumer purchasing habits.
Despite the name differences, the core performance of both types is still determined by technical parameters such as cable type, conductor material, and shielding design. Users shouldn’t dwell on terminology differences; instead, focus on the actual product specifications and performance. The following will provide an in-depth analysis of the key technical specifications of Ethernet cables.
Evaluation of Key Technical Indicators
Cable Category: Cat5, Cat5e and Above
Ethernet cables are commonly referred to as “Cat,” standing for Category. Common types include Cat5/5e and Cat6/6a. http://How to Choose the Right Cat5-5e, Cat6-6a, Cat7 and Cat8 Cables
Cat5: The long-standing Cat5 cable supports bandwidths up to 100Mbps and was suitable for home networks in the 2000s. However, with the rise of applications like 4K streaming and cloud gaming, its bandwidth bottleneck has become apparent. Even short transmission distances of 50 feet can cause actual data rates to drop due to crosstalk, and it has been phased out of the market.
Cat5e: Cat5e, the best replacement for Cat5, reduces crosstalk by over 50% through optimized twisting, supporting bandwidths up to 1Gbps. For 90% of home users, a 50-foot Cat5e cable is sufficient for 4K video streaming and multiple concurrent devices.
Cat6 and above: Cat6 cables boast bandwidths exceeding 10Gbps and incorporate stricter shielding to reduce crosstalk. Suitable for high-density data centers or 8K streaming scenarios. Some service rooms and streaming workers are also gradually upgrading to Cat6 or higher cables to support higher bandwidth requirements in the future.

Transmission Speed and Bandwidth Requirements
When choosing an Ethernet cable, it’s important to consider the device’s performance as the lower limit and future needs as the upper limit. You can check the manuals for your router, network card, or smart TV to confirm the maximum supported speed. If your device only supports 100M Ethernet, Cat5e is sufficient. For Gigabit Ethernet, at least Cat5e is required to achieve the full speed. For longer distances, consider Cat6 or higher cables. If you plan to add higher-bandwidth devices in the next 3-5 years, such as 8K TVs or 10G switches, you can directly choose Cat6 or higher cables to avoid duplicate wiring.
Construction Materials and Connector Quality
Cable durability and signal quality are largely dependent on the conductor, connector, and sheath materials.
Common conductor materials include pure copper and CCA (copper-clad aluminum). High-quality cables typically use pure copper conductors, which offer high conductivity and low resistance, making them suitable for long-term, high-load operation. Cheaper products, however, often use CCA. While lightweight and 30% less expensive, the aluminum core is susceptible to oxidation, increasing contact resistance and potentially causing intermittent disconnection after 2-3 years. Pure copper cable is recommended for long-term fixed wiring, while CCA can be considered for temporary wiring to reduce costs.

For the connector part, Ethernet cables usually use RJ45 crystal plugs. Some products currently use gold-plated contact design to reduce oxidation and corrosion. In humid environments or high-frequency plug-in scenarios, the thick gold plating layer can extend the service life.

The second is the outer sheath material. The choice of outer sheath material usually depends on the usage scenario. PVC outer sheath is soft, low cost, and suitable for indoor dry environments. LSZH outer sheath is fire retardant, environmentally friendly and non-toxic, making it the first choice for offices and data centers. In outdoor scenarios, cables with UV anti-aging layers and waterproof coatings are usually used for harsh environments.
Performance Factors for Reliable Connections
Signal Attenuation and Anti-Interference Capabilities
Signal attenuation refers to the reduction in signal strength during transmission due to resistive losses and electromagnetic radiation. The degree of attenuation in a 50ft cable is directly determined by the conductor material, wire gauge, and shielding design.
As mentioned earlier, pure copper conductors have lower resistance than CCA conductors. Secondly, regarding wire gauge, 24AWG has approximately 15% lower attenuation than 26AWG. According to IEEE standards, the maximum allowable attenuation for a 50ft Cat5e cable at 1Gbps is 4.5dB. High-quality pure copper cables typically have an attenuation of less than 3dB, barely affecting performance. CCA cables, on the other hand, may experience attenuation exceeding 5dB, resulting in occasional packet loss.
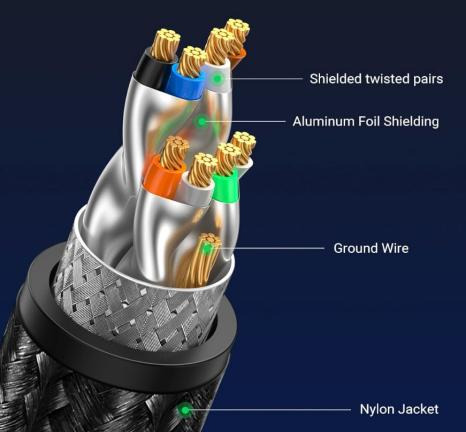
Shielding is crucial for interference resistance. Electromagnetic interference, such as from wireless routers and industrial motors, is common in the environment and can affect signal transmission quality. Some Cat5e cables use UTP, or unshielded twisted pair (UTP). This design is generally low-cost and lightweight, making it suitable for interference-free environments such as homes and offices. As long as it’s not laid alongside power lines, interference is negligible. The shielded twisted pair (STP) design increases anti-interference capability by 30% by adding an aluminum foil or braided mesh shielding layer, but at the cost of increased weight and reduced flexibility, making it suitable for high-interference scenarios such as factory workshops.
Trade-off Between Flexibility and Durability
In actual use, cable flexibility and durability are also factors to consider. Finding a balance between these two depends on the specific installation scenario.
Indoors, flexible, or soft, sheathing materials, such as PVC or flat wire, are preferred. These are more adaptable to practical scenarios and need to be routed around corners, furniture, or door cracks. In outdoor or industrial environments, cable durability is important. Cables typically need to withstand rain, UV rays, and temperature fluctuations. Cables with waterproof coatings or armor should be selected to provide a longer service life. For specialized scenarios, such as data centers and high-density racks, LSZH flame-retardant, low-smoke materials should be used to meet data center fire regulations.
Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Another important factor to consider is compatibility with existing equipment or cabling systems. Incompatibility can lead to connection failures.
Interface compatibility: Ethernet cables typically use the universal RJ45 connector. Some RJ45 connectors may have different pin thicknesses and jack tightness, which can affect contact reliability. Older equipment may experience poor contact with new cables due to oxidized pins, requiring extra care. Products with snap-on reinforcements can provide a stable connection.
PE power support: If the existing cabling environment needs to power devices such as IP cameras and AP panels, confirm that the cable supports the PoE standard.
If the existing cabling system already has pre-installed permanent wiring, ensure that the cables purchased are of the same standard. If Cat6 cables are pre-installed, purchasing Cat5e cables later can result in decreased overall network performance.
Choosing the Right Cable for a Specific Application
Home Network Setup
You need to choose a suitable 50ft Ethernet cable in different scenarios. The core needs of home users are the stability of multi-device connections and the convenience of plug-and-play. From the perspective of basic streaming and daily Internet access, Cat5e pure copper unshielded cable can meet the needs. The 1Gbps bandwidth is sufficient to support multiple devices to play 4K video simultaneously, and the 50ft length has no attenuation pressure in the cross-room connection from the living room to the bedroom. If you need scenarios such as e-sports or NAS storage devices that require low latency, you can upgrade to Cat5e cables with gold-plated RJ45 or Cat6 cables with better shielding, which can reduce electromagnetic interference and improve signal transmission quality. If there are too many smart devices and concealed wiring is required, you can choose ultra-thin flat cables, which do not affect the appearance and are easier to construct.
Office and Commercial Environments
In offices and commercial environments, network equipment is often densely populated and requires long operation times, resulting in high failure costs. Therefore, higher requirements are placed on Ethernet cables. Cat6 cables are typically used as standard, meeting 10G requirements. In high-density data centers, STP shielded cables or LSZH low-smoke halogen-free cables are often required to better shield crosstalk and comply with fire regulations.
Professional Application Scenarios
In industrial, outdoor, temporary deployment and other scenarios. Cables usually require extremely high durability and anti-destruction properties. In industrial environments, armored shielded cables and IP67 waterproof materials are required. They are able to withstand forklift crushing and humid and dusty environments, and can stably transmit signals under strong electromagnetic interference. Outdoor scenes usually need to consider the durability of the cable, and cables that support UV anti-aging and waterproof properties can be selected. In temporary deployment scenarios, low-cost cables made of CCA materials can be selected to reduce deployment costs and are suitable for short-term use and frequent replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can a 50-foot Cat5 Ethernet cable still be used? What’s the difference between it and Cat5e?
A: Cat5 cable theoretically supports 100Mbps bandwidth, but due to crosstalk, the actual transmission rate over a 50-foot distance is often less than 80Mbps, making it unsuitable for 4K streaming and other applications. Cat5e, through an optimized twisting process, supports 1Gbps bandwidth (250MHz), allowing stable full Gigabit speeds over a 50-foot distance. The price is only 10%-15% higher than Cat5, so we recommend upgrading to meet future needs.
Q: How should I choose between shielded (STP) and unshielded (UTP) cables?
A: It depends on the level of environmental interference. When near strong electromagnetic sources like power lines, motors, and microwave ovens, STP can reduce signal interference by over 70%, preventing latency fluctuations.
Q: Why are the prices of the same 50-foot cable so different?
A: The price difference mainly lies in the different core materials. Pure copper material is more expensive than CCA material, gold-plated process is more expensive than non-gold-plated industry, and the one with shielding layer is more expensive than the one without shielding layer. You can choose according to actual needs.








