Need a Fast 6ft Cat6 Ethernet Cable? Best Options for Stable Connections
What is a Network Cable?
Ethernet Cable is a kind of connecting cable that transmits network signals through physical media, mainly used for data communication between devices (e.g. routers, computers, switches, etc.), which forms the basis of wired network. Its core role is to convert electrical signals into data streams to achieve equipment interconnection, Internet access, LAN construction and other functions.
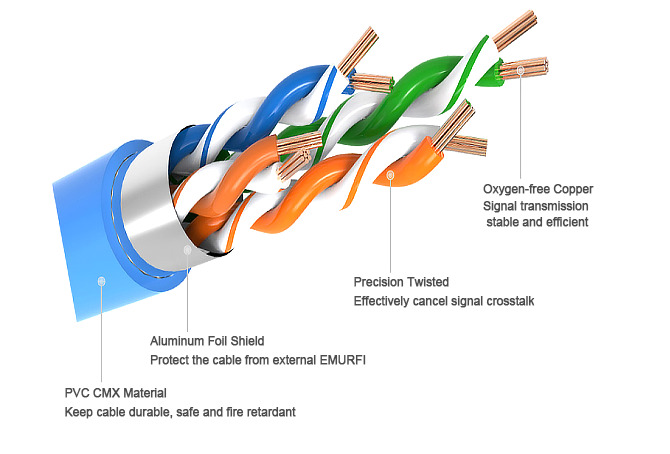
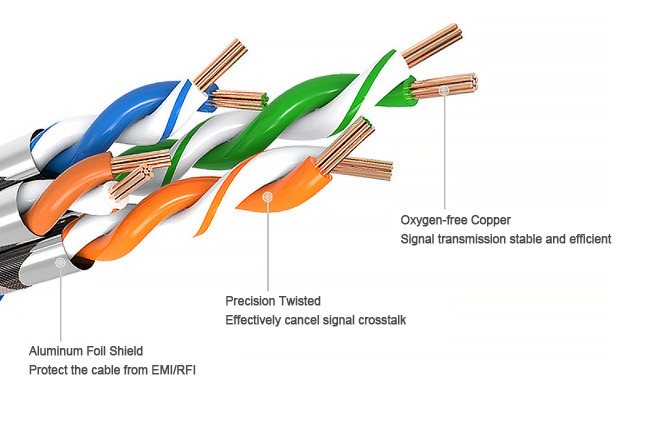
Because of its physical properties it is also called twisted pair cable, a data transmission line consisting of many pairs of wires. Two insulated copper wires are twisted around each other (generally counterclockwise) according to certain specifications to reduce the degree of signal interference. As the outer skin of the wire wrapped in two twisted, the formation of twisted pairs. Twisted pair and then connected to the RJ45 port is composed of network cable.

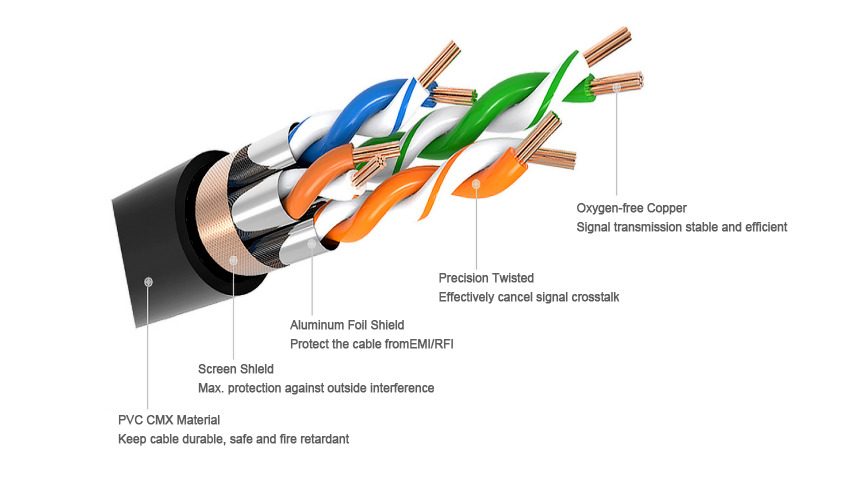
Network Cable Structure
Twisted Copper Wire
Common twisted-pair cables include 2 pairs of 4 wires (such as RJ-11 telephone wire) and 4 pairs of 8 wires (such as RJ-45 Ethernet cable).Twisted-pair cables were mainly used for transmitting analog signals in the past, but now they are also suitable for transmitting digital signals.
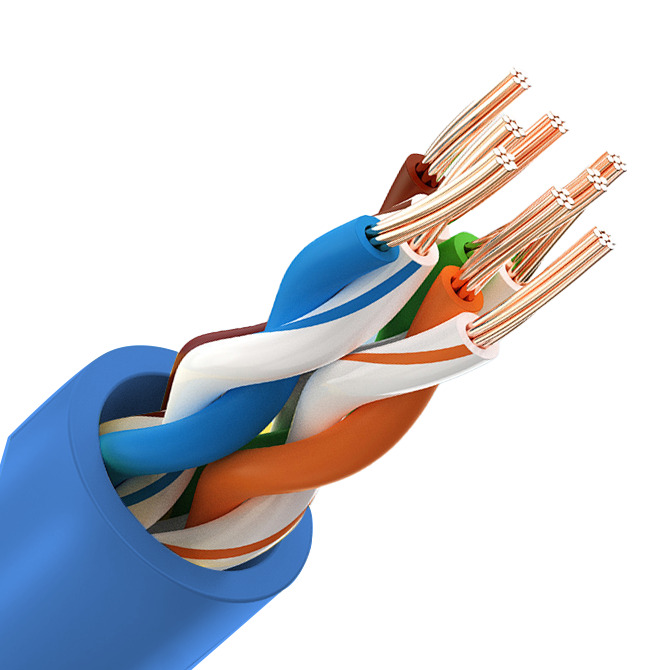
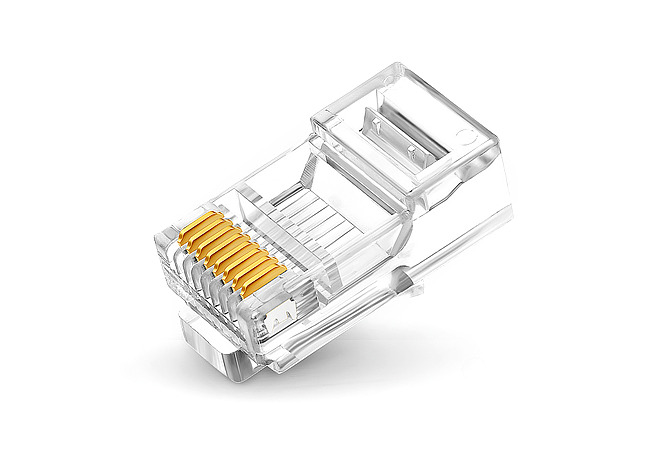
Registered Jack
The Registered jack is an important interface device in network connections. It is a plastic connector that can be inserted in a fixed direction and automatically prevent it from falling off.

Network Cable Type
Direct Twisted-Pair Connection
Both ends are twisted-pair cables of standard 568A or 568B (568B-568B is more common), which are used for interconnection of devices at different layers. Both ends of the network cable should be connected in accordance with the T568B network cable connection method. Terminal devices (such as personal PCS) – switch, PC – router, switch – camera.
Cross-Twisted Pair
One end is the 568A standard, and the other end is the 568B standard twisted-pair cable (568A-568B), which is used to connect the equipment on the same floor.
One end of the network cable is connected as T568A and the other end as T568B. In practical use, the application of cross-twisted pair cables is extremely rare.
Network Cable Polarity
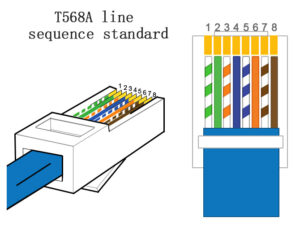
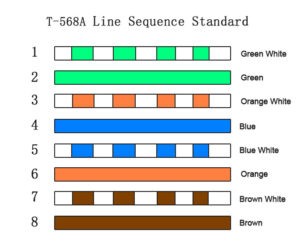
The polarity of network cables is divided into 568A and 568B. 568A corresponds to the wire colours green-white, green, orange-white, blue, blue-white, orange, brown-white, brown.
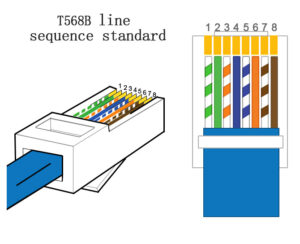
The wire colors corresponding to the 568B sequence are orange-white, orange, green-white, blue, blue-white, green, brown-white, and brown.
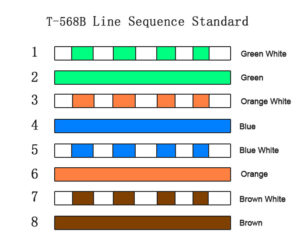
Network Cable Classification
Classified by Whether It is Shielded or Not
It is divided into two major categories: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP).
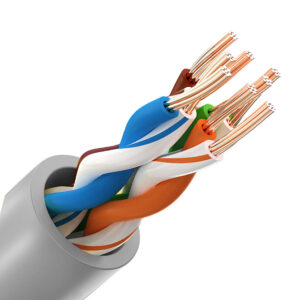
UTP: Unshielded Twisted Pair
FTP: Total Shielded Twisted Pair
Each pair of wires is not shielded separately.
STP: Shielded Twisted pair, that is, each pair of wires is shielded separately
SFTP: double shielded twisted pair, each pair of wires is individually shielded and then total shielding is applied.
Classification of Twisted Pair Cables According to Electrical Properties
It can be categorized into super category 5, category 6, super category 6, category 7 and category 8 twisted pair. The price difference between different categories of twisted pair is large or even disparate, and the range of applications is also very different. The higher the category, the less affected and attenuated it is, and the shorter the transmission distance.
| CAT5E | CAT6 | CAT6A | CAT7 | CAT8 | |
| transmission rate | 100M | 1000M | 10000M | 10000M | 25-40G |
| rate | 100MHz | 250MHz | 500MHz | 500-600MHz | 2000MHz |
| Shielding Type | FTP,UTP | SFIP,UTP | SFIP | SSTP,SFTP | SFIP |
| range of application | Gigabit network | Gigabit network | Gigabit network | Gigabit network | Gigabit network |
| conductor size | 24AWG (UTP)26AWG(FTP) | 24AWG (UTP),26AWG (SFTP),28AWG | 24AWG,26AWG | 26AWG | 28AWG |
| Material | PVC | PVC | PVC | PVC | PVC |
| transmission distance | 100m | 100m | 100m | 30m | 30m |
Classified by Purpose
They can be categorized into fine diameter network cables, multi-core network cables, and bulk network cables (network patch cables).
Fine diameter network cable is a kind of network cable on the basis of network patch cable. Distinguished according to the wire diameter of the network cable, the regular network cable wire diameter has 24AWG and 26AWG, the wire diameter of the fine diameter network cable is 28AWG, which is 41% of 24AWG. Fine gauge network cable mainly has CAT6, which can be widely used in RJ45 port devices, such as switches, computers, ADSL, etc.. Its advantage is stable transmission, strong and durable.
Multi-core network cables are mainly available in CAT5e and CAT6, CAT6a. for data centers. Pre-terminated backbone cable assemblies are available for Ethernet switches and enterprise servers, enabling direct cabling and cross cabling solutions for copper networks. Multi-core network cables can be connected directly to the modules or through a top-of-rack connection to a patch panel through which the cables are managed. Advantages include quick and easy installation, reduced labor costs; efficient management, and applicability to multiple density patch panels.
Bulk network cables are applied in engineering solutions, data centers, etc. Their advantages are flexible cable bodies and convenient wiring and installation. The material transmission of oxygen-free copper is stable. The length is free and can be cut at will. The high-density HDPE inner sheath is anti-corrosive and has good ductility.
What Speeds Can Achieve with Cat6 and How Can Increase My Internet Speed?
Theoretical Speed of Cat6 Network Cable
Network speeds of up to 10 Gbps can be achieved in an ideal environment with no interference and quality cables within 55 meters. 1 Gbps is supported within 100 meters. speeds of up to 10 Gbps can be achieved in an ideal environment with no interference and quality cables within 55 meters. its 250 MHz bandwidth significantly outperforms Cat5e’s 100 MHz, which reduces signal attenuation and crosstalk, ensuring its signal integrity.
How Can Increase the Speed of My 6-Foot Cat6 Ethernet Cable Network?
Cable quality and specifications
Poor quality cables may cause signal degradation and interference, which can be avoided by using regular brand Cat6 cables. Next, check the integrity of the cable to avoid bending, crushing or damage. Lastly, poor contact with the registered jack can affect the rate, and you need to check the quality of the RJ45 connector.
Network device configuration
To realize its full performance, make sure that the devices connected at both ends, such as computers, routers, switches, etc., support Gigabit or 10 Gigabit speeds. Also, outdated drivers can limit performance and require timely updating of network card drivers.
Interference or crosstalk
To avoid interference or crosstalk with Cat6 Ethernet cable signals, you need to stay away from sources of strong electromagnetic interference such as power lines, motors, microwave ovens, etc., and avoid tightly bundling with multiple network cables.
How Do Properly Install a 6-Foot Cat6 Ethernet Cable?
Cables and connectors
We recommend using RJ45 registered jack 24AWG Pure Copper Core Cat6 cable with dust jacket design, and if you need to crimp in the field, you can prepare crimping pliers and wire meter.
Wire sequence arrangement
recommends the T568B standard. Use a wire stripper to strip about 2cm of the outer jacket, arrange the 4 pairs of twisted pair wires in order, and trim about 1.5cm lengths of the wires, which can snag the registered jack by the outer jacket.
Crimping technology
Insert the arranged wires into the RJ45 header and crimp them with crimping pliers, hearing the “click” sound indicates that they are in place. Check whether all the copper pins are completely downward pressure and whether the outer skin is fixed by the registered jack end card.
Connection and testing
After completion you can detect whether it is connected by observing the device indicator, Gigabit connection has green or blue constant light, the color of the indicator may be different for different devices. Or use a wire meter to verify, connect both ends of the cable to the wire meter, and make sure the 1-8 indicator lights are on in sequence. You can also verify this in the system by going to:
Windows: control panel – network status – view connection speed.
MacOS: system information – network – current link speed.
How to Choose the Best Cat6 Ethernet Cable?
Core material
Pure copper is superior to copper-clad aluminum, and copper-clad aluminum is superior to copper-clad steel. The advantages of pure copper are low resistance and high speed, suitable for long distance transmission and PoE power supply. Copper-clad aluminum and copper-clad steel are low in price and high in resistance, and are not recommended for PoE.
Shielding types
UTP for flexible and less interference resistant environments such as homes, offices, etc. FTP for medium interference environments near power lines, which reduces EMI interference. STP for high interference environments in factories or server rooms.
Wire gauge
23AWG is characterized by thick gauge and low resistance for long distances and PoE. 24AWG is suitable for distances up to 50 meters. 28AWG thin wire is only suitable for short patch cords, not for trunk cabling.
Certification standards
The basis for judging whether the cable meets the Cat6 performance standard is whether the product has passed the TIA/EIA-568-C.2 or ISO/IEC 11801 international certification. Some products will also pass third-party certifications such as UL,CE and FCC.
FAQ
Q: What is the maximum speed supported by a 6-foot Cat6 network cable?
A: For a short distance of 55 meters, it supports 10 gigabit 10Gbps; for a long distance of 100 meters, it supports 1 gigabit 1Gbps. The actual speed is affected by device limitations. For instance, routers or network cards only support 1 GBPS and cannot reach 10 GBPS.
Q: What are the differences between Cat6 and Cat5e?
A: The maximum transmission rate of Cat5e is 1Gbps, with a bandwidth of 100 MHz. It features a common twisted pair design for crosstalk suppression and a 24AWG wire gauge. Cat6 has a rate of 1Gbps, short-range support of 10Gbps, a bandwidth of 250 MHz, cross-skeleton crosstalk suppression, and 23AWG wire gauge.
Q: What scenarios are suitable for a 6-foot Cat6 line?
A: Short-distance high-speed connections such as computers – routers or switches, game consoles – network devices, switches -NAS/ servers; PoE power supply devices such as IP cameras, wireless aps, etc.
Q: How to judge the quality of Cat6 wire?
A: It can be done by looking at the logo certification, measuring the resistance, checking the cross-shaped skeleton and brand selection.
Q: Why is my Cat6 line speed only 100Mbps?
A: The reasons might be incorrect wire sequence, inferior registered jack, equipment limitations, cable damage, etc. Use a wire tester to check the connectivity of the 8 cores, replace the router or network card, and re-press the Registered jack.
Q: Which is better, flat Cat6 or round Cat6?
A: Flat Cat6 is easy to wire and has an attractive appearance, but it has slightly weaker anti-interference ability and is not suitable for long distances. Round wire Cat6 has strong anti-interference ability and is suitable for PoE. It is recommended to choose flat Cat6 cables for short-distance household use, and round Cat6 cables for high-speed or PoE applications.
Q: Can Cat6 be used for PoE power?
A: Sure, but it should be noted that pure copper wire with stable power supply must be used. It is recommended to use 23AWG wire gauge, and the distance should be between 50 and 100 meters.
Q: How to extend 6 feet Cat6 cable?
A: It is not recommended to extend it in series. It is suggested to replace it with a longer single wire, such as directly replacing it with a 10-foot Cat6. It is also possible to add a gigabit switch in the middle or use optical fiber and media converter in combination for an extremely long distance.
In This Article
- 1 What is a Network Cable?
- 2 Network Cable Structure
- 3 Network Cable Type
- 4 Network Cable Polarity
- 5 Network Cable Classification
- 6 What Speeds Can Achieve with Cat6 and How Can Increase My Internet Speed?
- 7 How Do Properly Install a 6-Foot Cat6 Ethernet Cable?
- 8 How to Choose the Best Cat6 Ethernet Cable?
- 9 FAQ
Show All
Collapse








