Detailed Explanation of SFP Optical Module Packaging
In the field of optical communication, optical transceivers, as the core devices for optical-electrical signal conversion, play a crucial role in driving technological advancement and application expansion across the entire industry through the development and innovation of their packaging forms. The SFP series packaging, with its compact size, flexible compatibility, and continuously improving performance, has become a highly recognized and important branch in the optical transceiver market.
SFP(Small Form-factor Pluggable)
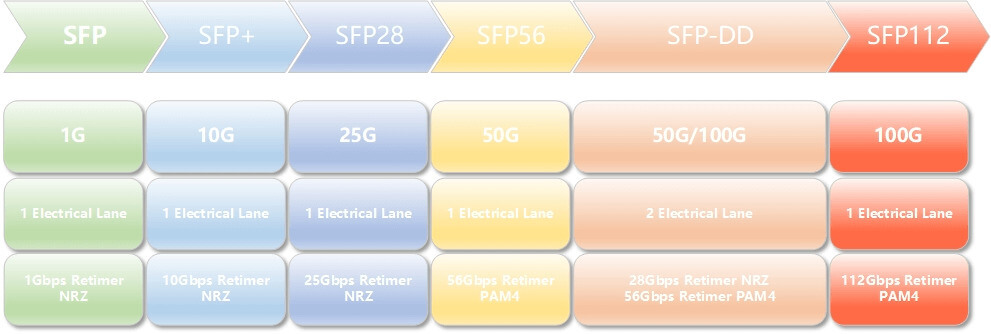
SFP, short for Small Form-factor Pluggable, is one of the most widely used packaging types today. It is a small form-factor hot-pluggable optical module standard introduced by the MSA organization in 2001. Its emergence completely solved the issue of the large size of traditional optical transceivers. Compared with the earlier GBIC, its size was reduced by approximately 50%, significantly increasing device port density and greatly facilitating equipment installation and maintenance.
SFP optical modules support multiple data rates, including 155Mbps, 622Mbps, 1.25Gbps, and 2.5Gbps, and are applicable to a variety of communication protocols such as Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and SDH/SONET. They adopt LC fiber connectors, support both multimode fiber and single-mode fiber, and cover transmission distances ranging from several hundred meters to tens of kilometers. The hot-pluggable feature of SFP allows modules to be conveniently replaced or upgraded without interrupting system operation, greatly improving system maintenance efficiency.
Thanks to their standardized design, SFP optical modules from different manufacturers maintain good compatibility, making SFP packaging widely adopted in the market and the mainstream choice for 1G and 2.5G data rates.
SFP+(Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus)
SFP+ is an enhanced version of SFP, which increases the data rate to 10Gbps while maintaining the same form factor as SFP, and it also supports hot-plugging. It is compatible with SFP slots, enabling smooth upgrades for existing equipment. In terms of transmission media, SFP+ optical modules not only support traditional fiber transmission but also introduce high-speed cable solutions such as DAC and AOC, meeting the requirements of short-distance high-speed transmission in terms of cost and power consumption. They are widely used in scenarios such as intra–data center server interconnection and storage area networks.
SFP28(Small Form-factor Pluggable 28G)
SFP28 is an optical module form factor designed for 25Gbps data rates, representing a further evolution of the SFP series. Its dimensions are identical to those of SFP and SFP+, maintaining excellent compatibility and the advantages of miniaturization. By improving signal transmission technology, SFP28 optical modules support 25Gbps high-speed transmission and are primarily applied in 25G Ethernet. They play an important role in intra–data center interconnections, providing a compact and cost-effective solution for high-speed connectivity between servers and switches.
SFP56(Small Form-factor Pluggable 56G)
SFP56 is an optical module form factor designed for a single-channel data rate of 56Gbps, supporting 50Gbps transmission speeds. It represents an important evolution of the SFP series in the field of ultra–high-speed data rates. While maintaining the same physical dimensions as traditional SFP, it achieves a significant increase in speed through optimized signal transmission and modulation technologies. SFP56 optical modules are mainly used for 50G Ethernet connections as well as higher-level interconnects within data centers.
SFP-DD(Small Form-factor Pluggable-Double Density)
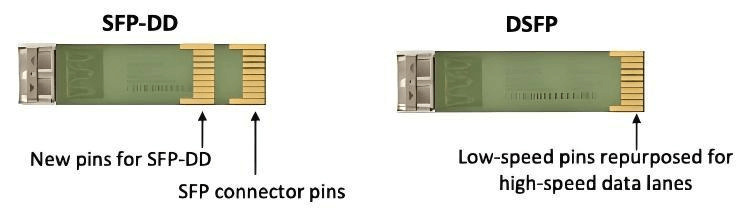
SFP-DD, or Small Form-Factor Pluggable Double Density, is a hot-pluggable optical module form factor introduced to meet the demands of higher port density and higher data rates. While maintaining the same physical dimensions as traditional SFP modules, it integrates two electrical lanes internally, doubling the data rate by increasing pin density. Using NRZ modulation, it supports 25Gbps per channel, while with PAM4 modulation it can achieve 56Gbps or 112Gbps per channel, significantly improving port utilization and enabling data rate upgrades.
DSFP(Dual Chanel Small Form-factor Pluggable)
DSFP, or Dual-Channel SFP, is designed on the basis of the SFP form factor and achieves dual-lane signal transmission through two independent electrical channels, making it a dual-transmit dual-receive optical module. Like SFP-DD, DSFP also supports NRZ and PAM4 modulation to achieve different data rates. However, unlike SFP-DD, which is based on a single optical channel, DSFP uses dual optical channels, with a different implementation method. Both DSFP and SFP-DD provide high-density, high-speed data transmission, offering users more options.
SFP112(Small Form-factor Pluggable 112G)
SFP112 is an optical module form factor designed for 100Gbps data rates, representing an extension of the SFP series into the ultra-high-speed domain. By adopting advanced PAM4 modulation technology and high-speed signal processing chips, it achieves a single-channel transmission rate of 100Gbps. The package size remains the same as that of traditional SFP, enabling high-density deployment within existing equipment architectures. The SFP112 form factor is primarily used in 100G Ethernet connections as well as in higher-level network architectures.
- PREV: Analysis of Less Common Optical Transceiver Form Factors
- NEXT: Null
In This Article
- 1 SFP(Small Form-factor Pluggable)
- 2 SFP+(Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus)
- 3 SFP28(Small Form-factor Pluggable 28G)
- 4 SFP56(Small Form-factor Pluggable 56G)
- 5 SFP-DD(Small Form-factor Pluggable-Double Density)
- 6 DSFP(Dual Chanel Small Form-factor Pluggable)
- 7 SFP112(Small Form-factor Pluggable 112G)
Show All
Collapse








